Unlocking the Potential of Gluten Feed in Livestock Nutrition
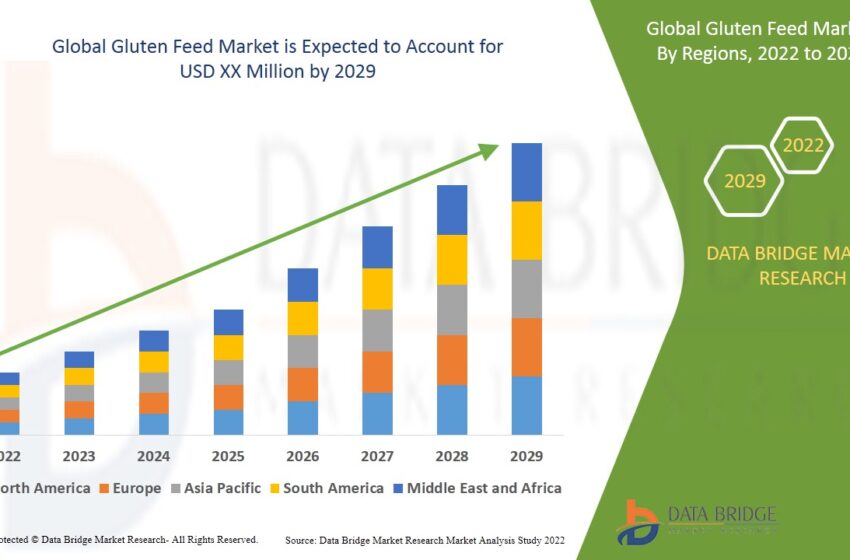
Introduction
In the realm of animal nutrition and sustainable agriculture, gluten feed stands as a hidden gem. Derived from the byproducts of the grain milling process, it’s a valuable source of nutrition for livestock, particularly cattle and poultry. Yet, it remains relatively unknown to many. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of gluten feed, exploring its nutritional composition, applications, environmental benefits, and its role in promoting sustainable farming practices.
What is Gluten Feed?
Gluten feed is a co-product of the grain milling process, typically derived from corn or wheat. It is produced by taking the remnants of grains left after the extraction of starch and gluten, which are the valuable components used in various food and industrial products. These remnants are often referred to as “wet feed” or “distillers’ feed” and are then dried and processed into the final gluten feed product.
Gluten feed is known for its high protein content, making it a valuable source of nutrition for livestock, particularly for cattle and poultry. It also contains dietary fiber, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to the overall nutritional value of animal diets. This nutrient-rich feed is used to enhance protein intake, support growth, and improve feed efficiency in livestock. It plays a vital role in animal nutrition and is utilized in feedlot operations, forage-based diets, and poultry nutrition.
Additionally, gluten feed offers sustainability benefits as it helps reduce food waste and maximize resource efficiency. It utilizes the byproducts of grain milling, contributing to reduced environmental impact, cost-effective animal nutrition, and a more responsible approach to agricultural practices.
What is Gluten Made Of?
Gluten is a protein composite found in wheat and related grains, including barley, rye, and spelt. It is a major component of wheat flour and gives dough its elasticity and strength, allowing it to rise and maintain its shape during baking. Gluten is made up of two main proteins:
- Gliadin: Gliadin is a protein fraction found in gluten that contributes to the dough’s extensibility, allowing it to stretch. It is primarily responsible for the dough’s ability to rise and capture gas produced during fermentation.
- Glutenin: Glutenin is another protein fraction in gluten, and it provides dough with its elasticity. This elasticity allows the dough to hold its shape and gives bread its chewy texture.
When water is added to flour, gluten forms as the proteins gliadin and glutenin interact. This interaction leads to the formation of a network of proteins that trap carbon dioxide produced by yeast during fermentation, causing the dough to rise and create a light, airy structure in baked goods.
Gluten is a critical component in many baked products, including bread, pizza, and various pastries, as it imparts the desired texture and structure to these foods. However, some individuals have gluten-related disorders, such as celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and must avoid gluten-containing products in their diet.
Benefits of Gluten in Food Production
Gluten, the protein composite found in wheat and related grains, offers several benefits in the context of food production:
- Dough Elasticity: Gluten provides dough with its elasticity, allowing it to stretch and rise during the fermentation process. This is particularly valuable in bread-making, as it creates the characteristic texture and structure of bread, giving it a chewy and airy quality.
- Bread Volume: Gluten plays a key role in capturing and retaining carbon dioxide produced by yeast during fermentation. This results in increased bread volume and a light, fluffy texture, making bread more appealing and palatable.
- Improved Texture: In addition to bread, gluten is used in various baked goods, such as cakes, cookies, and pastries, to improve their texture. It helps create a tender, moist, and crumbly texture in these products, enhancing their overall quality.
- Binding Agent: Gluten serves as a binding agent in food products. It can help bind ingredients together, improving the cohesiveness of mixtures and preventing ingredients from separating during cooking or baking.
- Protein Content: Gluten contributes to the protein content of wheat-based foods, which is an essential nutrient for human nutrition. Wheat and wheat-based products are significant sources of protein in many diets worldwide.
- Versatility: Gluten is a versatile ingredient that can be modified and processed in various ways to create a wide range of food products. This versatility makes it a valuable component in the food industry, enabling the production of diverse items from bread to pasta.
It’s important to note that while gluten has many benefits in food production, it can also pose health concerns for individuals with gluten-related disorders, such as celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity. For these individuals, gluten consumption can lead to adverse health effects, and they must avoid gluten-containing foods.
Challenges and Considerations
While gluten feed offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consider some challenges, including storage and handling requirements, potential spoilage, and variations in nutritional content.
Conclusion
Gluten feed, derived from grain milling byproducts, is a valuable but often underestimated resource in animal nutrition and sustainable agriculture. With its rich nutritional composition, applications in cattle and poultry diets, and positive environmental impact, it plays a crucial role in promoting resource-efficient and eco-conscious farming practices.
In conclusion, gluten feed is a versatile solution for improving livestock nutrition and contributing to a more sustainable and responsible agricultural industry.
For further insights on agriculture, animal nutrition, and sustainability, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-gluten-feed-market
